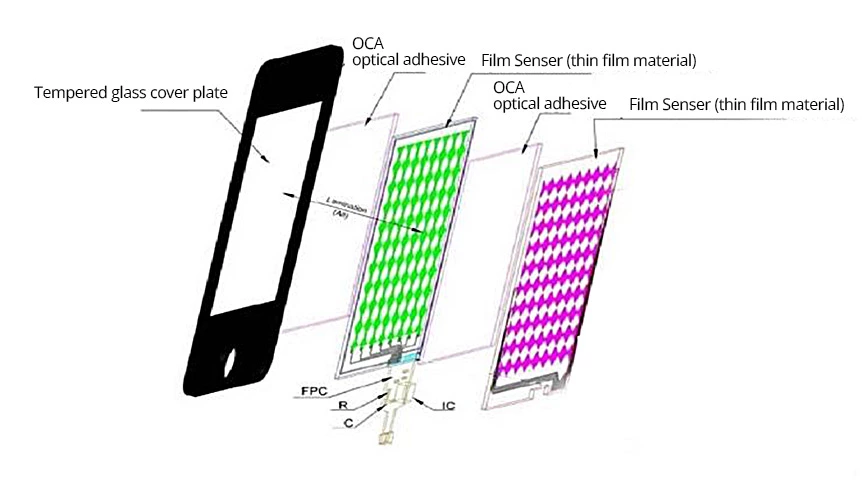
Introduction to IPS LCD Panels and Wide Viewing Angle Technology
The use of wide-viewing-angle design in terminal product screens aims to allow users to view display content from any angle. This feature enhances the product's viewing angles and increases screen contrast, color effects, and brightness. Displays with this design are called IPS LCD panels.
In-Plane-Switching Mode LCD
Normally Black Mode
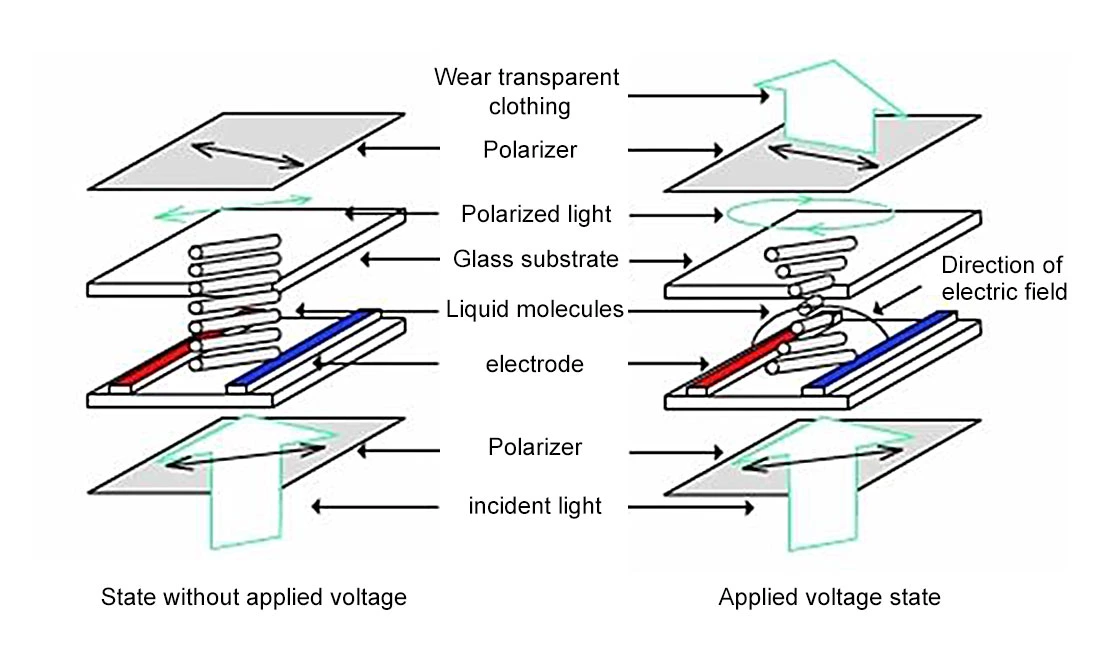
In-Plane Switching (IPS LCD)
IPS LCD panels, developed by Hitachi in 1996, were designed to improve the poor viewing angles and color reproduction of TN panels. The name "In-Plane Switching" comes from the main difference compared to TN panels: the electrodes are on the same plane, unlike other panels where electrodes are arranged vertically. The crystal molecules move parallel to the panel plane, unlike other panels where they move vertically.
This change reduces light scattering in the matrix, giving IPS panels ultra-wide viewing angles and excellent color representation. The first generation of IPS technology had drawbacks such as slow response time and low contrast, but later versions significantly improved these issues. IPS panels offer wide-viewing-angle technology and accurate color reproduction, with almost no color shift at different angles. As a result, IPS panels are widely used in high-end displays for professional graphic artists. Despite recent price drops, IPS panels remain a mainstream product in the market.
IPS LCD Panels
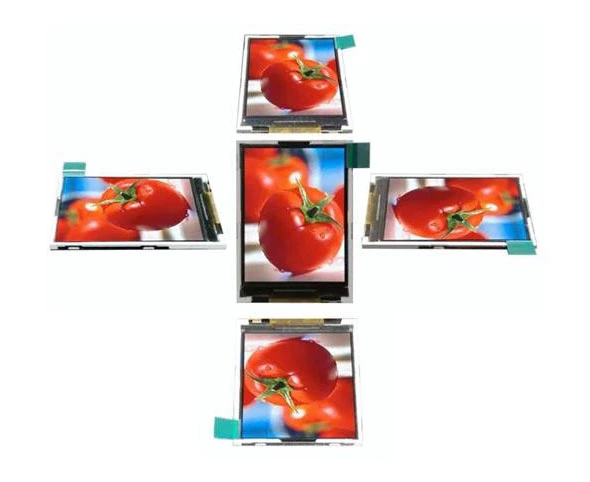

With wide-viewing-angle technology, they provide a perfect display effect with a 178-degree all-around view and flawless color presentation.