Comprehensive Guide to LCD Classification
Technology News
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) is a matrix display driven by thin-film transistors (TFT) that uses electric current to stimulate liquid crystal molecules, creating pixels, lines, and areas in combination with an LED backlight to form the display image. Here, we explore various dimensions for classifying LCD screens:

By Display Characteristics:
- High Brightness Displays: Brightness over 500 cd/m² for outdoor visibility.
- Full Viewing Angle LCDs: High contrast, color saturation, and dynamic clarity.
- Wide Temperature LCDs: Operate in harsh temperatures from -30°C to +85°C.
- Semi-Reflective Screens: Excellent visibility in both strong light and low-light conditions.
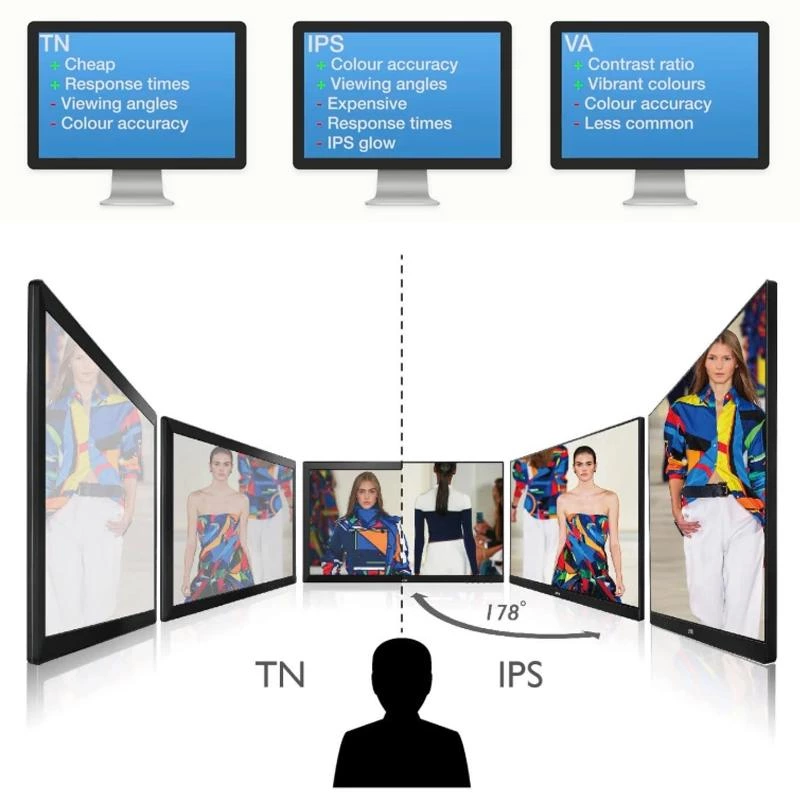
By Panel Type:
- TN (Twisted Nematic): Simple, cost-effective with high transmittance.
- IPS (In-Plane Switching): Superior color reproduction and wide viewing angles.
- VA (Vertical Alignment): High contrast and wide viewing angles, preferred for large displays.
By Interface Type:
- Common interfaces include RGB, SPI, MCU, MIPI, LVDS, and others like HDMI, TTL, and STN.
By Driving Method:
- Static Drive
- Simple Matrix Drive
- Active Matrix Drive
By Application Field:
- Household appliances, automotive displays, commercial displays, medical displays, industrial displays, instruments, and outdoor handheld devices.
Shenzhen DISEA Electronics is a professional LCD manufacturer offering a wide range of LCD displays and solutions tailored to various applications.