Causes, Principle Analysis, and Solutions for LCD Screen Flickering
When using display devices such as mobile phones, car displays, and household appliances, you might occasionally notice lines scrolling up and down the screen or see the screen flickering. This is known as the flickering phenomenon of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screens. Here, we'll explain the causes, principles, and solutions for LCD screen flicker.
Causes of LCD Screen Flicker
- Frequency Similarity between Screen and Ambient Light: The flicker can occur if the frequency of the screen light source is close to that of the ambient light source. Typically, these frequencies differ, but occasionally they might coincide, causing flickering.
- Mismatched LCD Module and Main Board: Flickering may also result from poor compatibility between the LCD screen module and the device's main board.
- Backlight Source Issues: The most common cause of flicker is the LCD screen's backlight source.
Principle Analysis of Backlight-Induced Flicker
LCD screens use two main types of backlight sources: LED (Light Emitting Diode) and CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp).
- LED Backlight: LED backlights are favored due to their low power consumption, low heat generation, high brightness, and long lifespan. However, they are more prone to flickering, especially noticeable to those with sensitive eyes, potentially causing discomfort or eye strain over prolonged use.
- CCFL Backlight: CCFL backlights also use PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for dimming, but the flicker is less noticeable due to the inherent delay in the phosphorescence of the fluorescent lamps, which causes a "persistence of vision" effect.
Understanding PWM Dimming
The brightness of an LED backlight is constant. To adjust the brightness of an LCD screen, the LED backlight is repeatedly turned on and off. By adjusting the length of the on and off times, the screen brightness is modulated. When users adjust the brightness, they are actually changing the duration of the backlight's on and off times, a method known as PWM dimming.
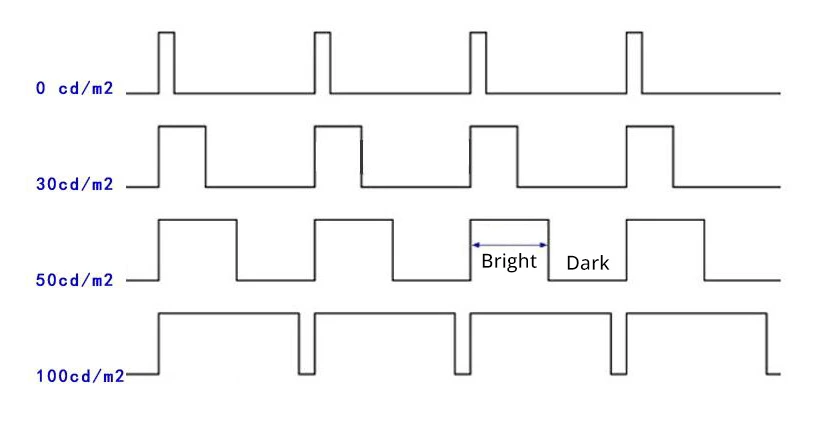
In practical applications of display products, the switching time of the LED backlight is very fast. Displays using PWM dimming typically operate at frequencies between 200Hz and 1000Hz. At frequencies above 100Hz, the human eye can hardly perceive any brightness changes, and the image appears continuously lit. Although CCFL backlights also use PWM dimming, CCFLs are essentially cold cathode fluorescent lamps. The process of electrons hitting the phosphor in the lamp to form a light spot has a delay effect, creating an afterglow effect. Therefore, the flickering issue with CCFL backlights is relatively better. While LCD backlights do have flickering issues, they are most noticeable at low brightness levels and thus do not affect their status as the mainstream backlight technology.
Solutions for LCD Screen Flicker
To address the flickering issue of LCD screens caused by the backlight, one solution is to use high-frequency PWM dimming. As mentioned earlier, common LCD display products operate at frequencies between 200Hz and 1000Hz. In some display fields where display quality is particularly critical, the operating frequency can be increased to 5000Hz or even higher, making the flickering imperceptible to the human eye and effectively eliminating the flicker issue of LCD screens.
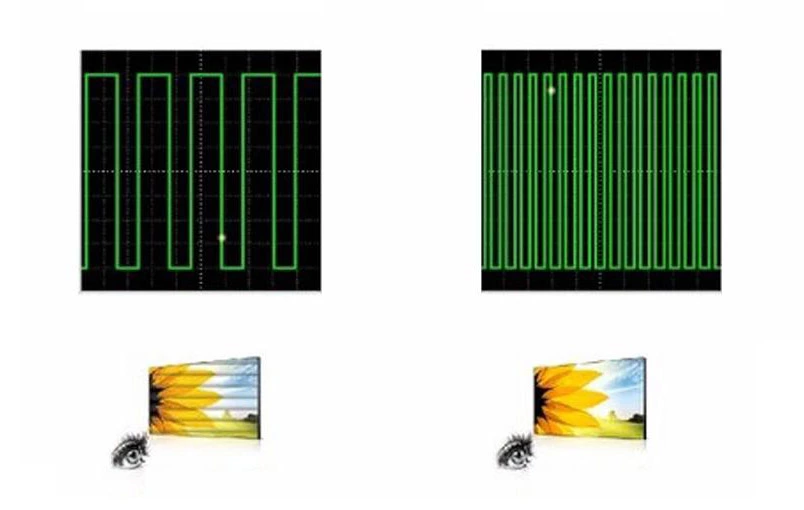
However, high-frequency PWM dimming needs to be used appropriately. It is important to consider product requirements, costs, display effects, and other factors comprehensively to determine the optimal solution.